Actions & Tools
Actions are custom skills you teach your AI agent, allowing it to go beyond answering questions and actually do things — like fetching product prices, querying databases, submitting forms, or triggering workflows in external services.
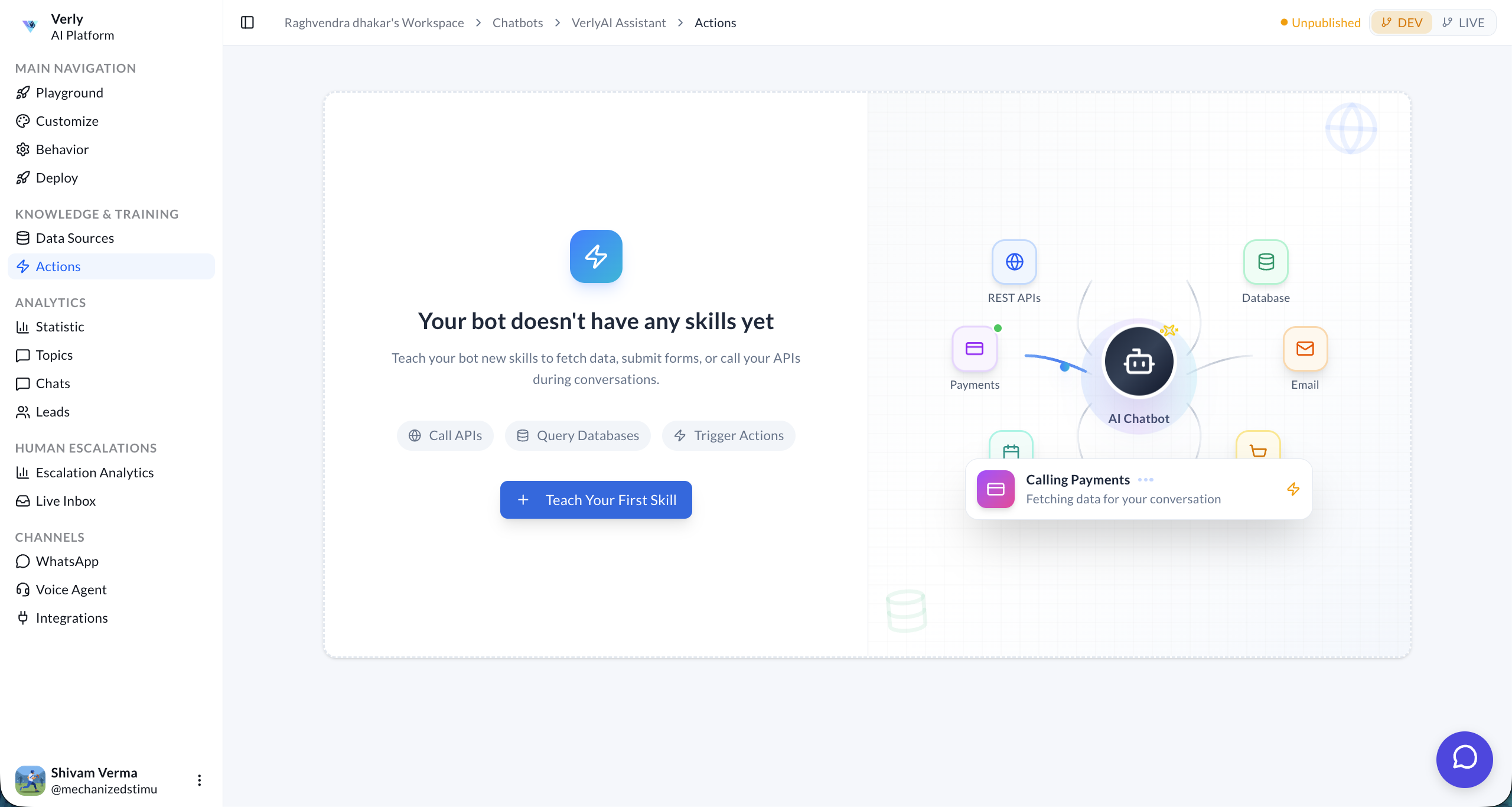
When your bot doesn't have any actions yet, you'll see the "Teach Your First Skill" prompt. You can create actions that:
- Call APIs — Fetch live data from any REST endpoint.
- Query Databases — Look up records from your internal systems.
- Trigger Actions — Fire off automations, send emails, create records.
Click + Teach Your First Skill to open the Action Builder wizard.
Creating a New Action
The Action Builder is a 5-step wizard: General → API → Inputs → Test response → Data access.
Step 1: General
Define the core identity of your action — what it is and when the AI should use it.
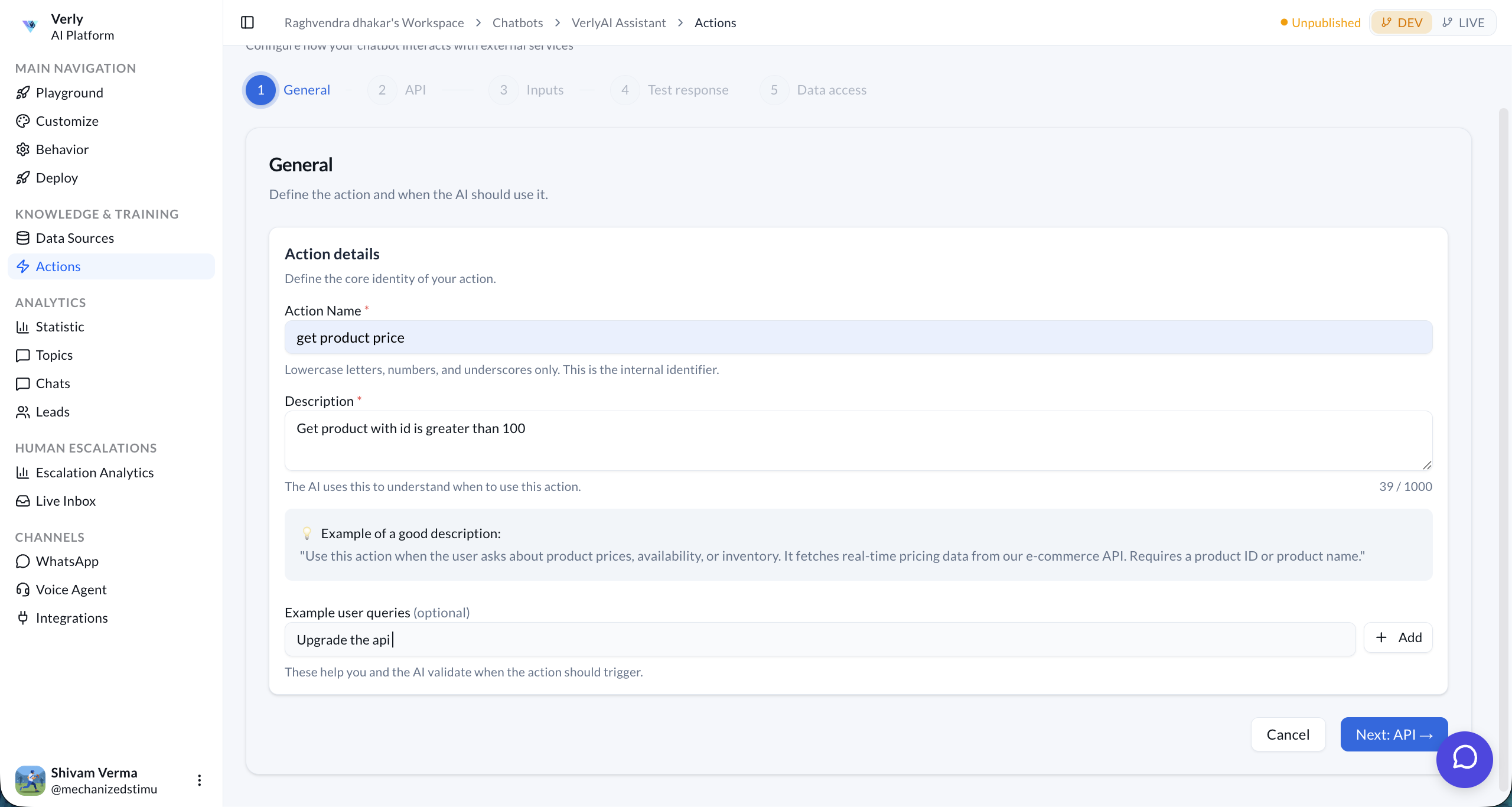
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Action Name | A unique identifier using lowercase letters, numbers, and underscores (e.g., get_product_price). |
| Description | Tells the AI when to trigger this action. Write it clearly so the model understands the context. |
| Example User Queries | Optional sample messages that help the AI learn when to trigger the action (e.g., "What's the price of item X?"). |
Click Next: API → to continue.
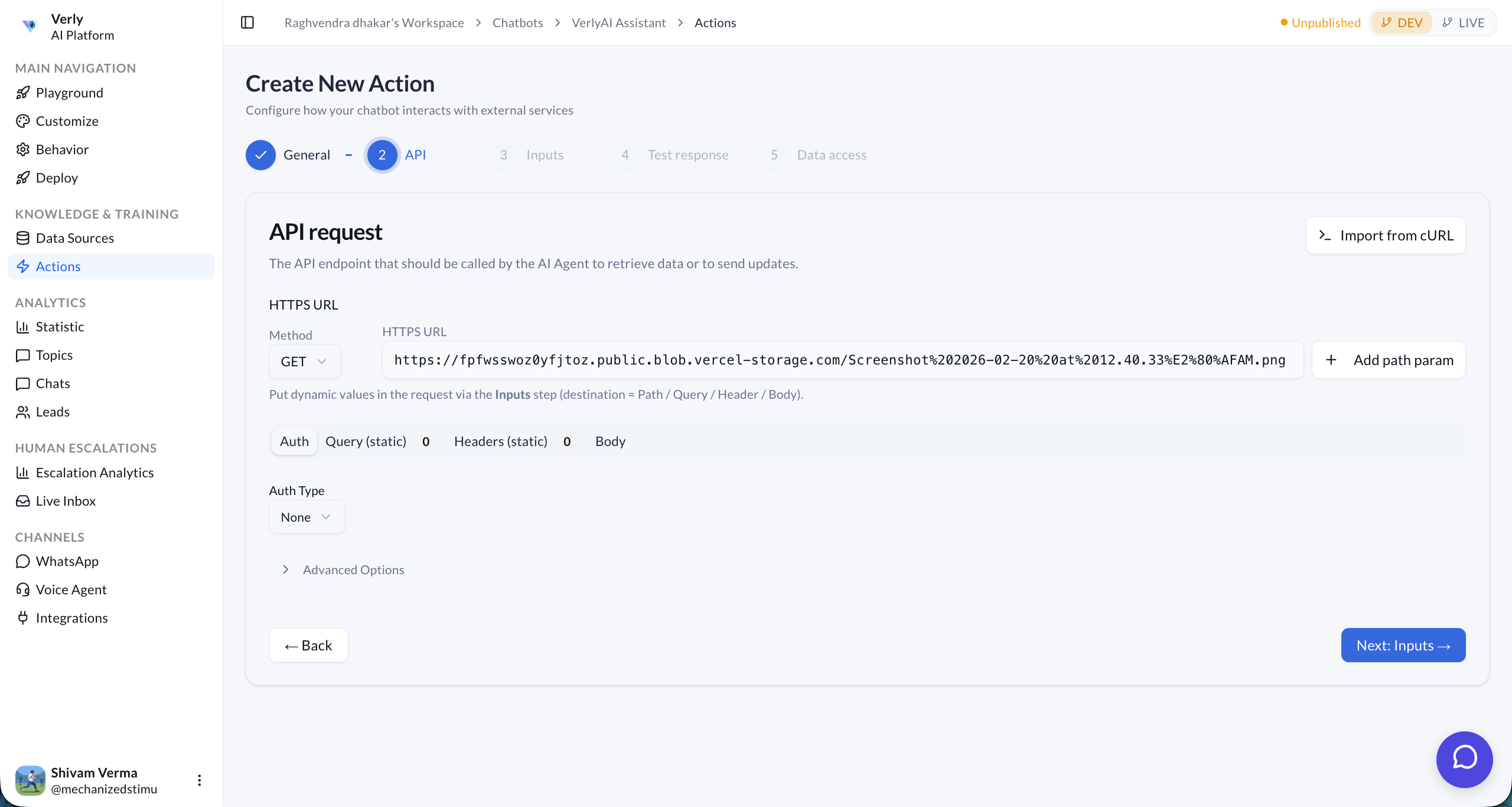
Step 2: API
Configure the HTTP endpoint your agent will call.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Method | HTTP method: GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, or DELETE. |
| HTTPS URL | The full endpoint URL. Use {param} placeholders for dynamic path segments (e.g., /v1/products/{id}). |
| Auth | Authentication type: None, Bearer Token, API Key, or Basic Auth. |
| Query (static) | Static query parameters appended to every request. |
| Headers (static) | Static headers like Content-Type or custom API headers. |
| Body | For POST/PUT requests, define the request body structure. |
Import from cURL
You can quickly populate the API configuration by pasting a cURL command. Click > Import from cURL, paste your command, and hit Parse cURL.
# Example cURL to import
curl -X POST https://api.example.com/v1/users \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer token' \
-d '{...}'
Click Next: Inputs → to continue.
Step 3: Inputs (Parameters)
Define what information the AI needs to extract from the user's message and pass to the API.
For each parameter, you configure:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The variable name referenced in the URL or body (e.g., product_id). |
| Type | Data type: String, Number, Boolean, Array. |
| Description | Helps the AI understand how to extract this value from conversation. |
| Required | Whether the parameter must be collected before the action can run. |
| Default value | Optional fallback if the user doesn't provide the value. |
| Destination | Where the value is sent: Path, Query, Header, or Body. |
| Query key | The key name used in the query string (e.g., ?product_id=...). |
| Allowed Values | Restrict input to specific values (e.g., USD, EUR, GBP for a currency field). |
Click + Add Another Parameter to add multiple inputs. Click Next: Test response → when done.
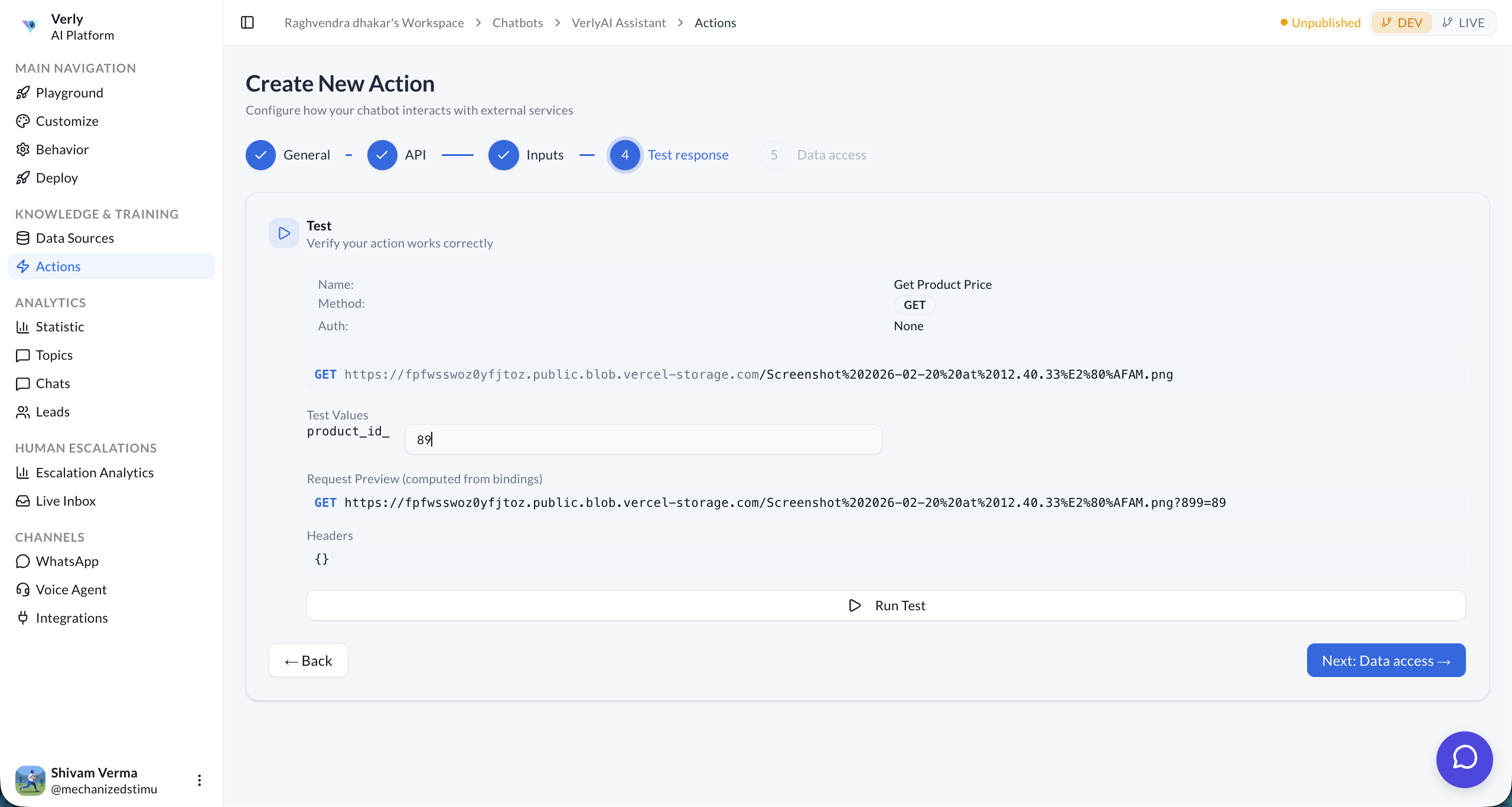
Step 4: Test Response
Before saving, verify your action works correctly by running a live test.
The test panel shows:
- Action Name & Method — Confirmation of what will be called.
- Test Values — Fill in sample parameter values (e.g.,
product_id: 7823). - Request Preview — Shows the exact URL that will be called with your test values.
- Headers — Displays the headers that will be sent.
Click ▷ Run Test to execute the API call. If the response looks correct, click Next: Data access →.
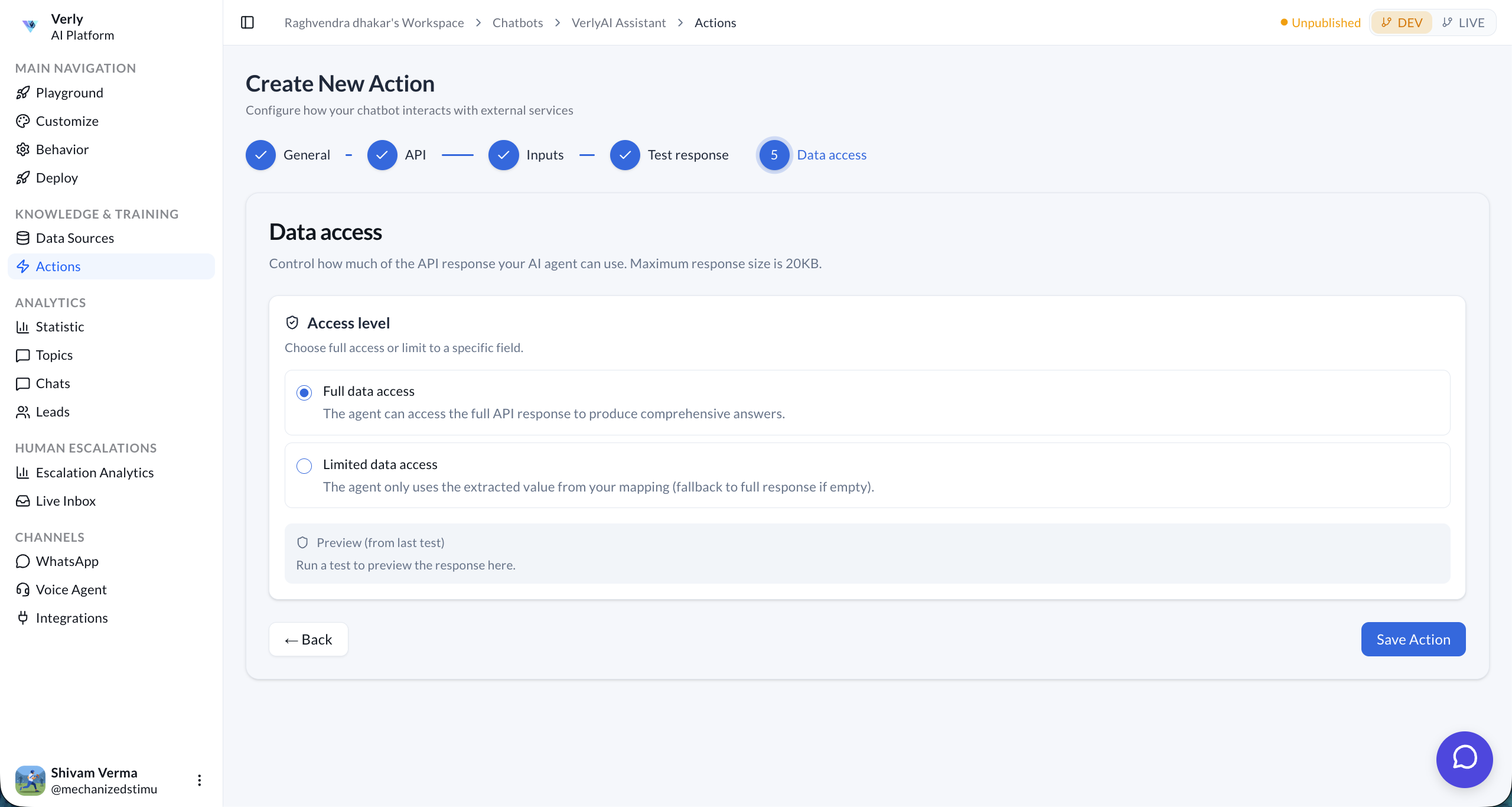
Step 5: Data Access
Control how much of the API response your AI agent is allowed to use.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Full data access | The agent can read the entire API response (up to 20KB) to formulate its answer. |
| Limited data access | The agent only uses a specific extracted field you map. Falls back to the full response if the field is empty. |
price or status. This keeps responses fast and focused.Click Save Action to finish. Your action is now available to the agent.
How Actions Are Triggered
Once saved, the agent automatically triggers an action during a conversation when:
- The user's message matches the description or example queries you provided.
- The AI extracts the required parameters from the conversation.
- The API call is made in real-time.
- The response is returned and the agent uses it to craft a reply.